Aloitan katsoa näitä 2.1. 2025 GeneCards listasta. (Etsin myös löytöjä, miten voi elämäntapaohjein ja ravinnon avulla pitää huolta silmänsä optisten kudosten pysymisestä funktionaalisina. Tässä on vasta perustavaa pohjatietojen etsintää 2.1. 2025)
https://www.genecards.org/Search/Keyword?queryString=Crystallins
(Mitä kystalliinit ovat? Ensimmäisestä krystalliinista sitaatti:Nisäkkäitten silmän linssin krystalliinit on jaettu kolmeen perheeseen: alfakrystalliinit, beetakrystalliinit ja gammakrystalliinit.
Alfakrystalliineja on kaksi geenituotetta , alfa-A ja alfa-B, asidinen ja baasinen. Ne muodostavat heterogeenisia aggrekaatteja (3:1), jotka toimivat ikäänkuin kaitsijaproteiinit, mutta niiden tehtävänä on pitää eri proteiineja liukoisena. Alfa-A esiintyy silmän linssissä ja alfa-B voi esiintyä laajasti muissakin kudoksissa ja elimissä. Silmän linssissä ei ole metabolista turn over- tapahtumaa, joten krystalliiniproteiineissa heijastuu ikämuutokset ja ikävaiheet. Krystalliinit ovat olennaisia silmän linssin läpinäkyvyydelle.
-
Mammalian lens crystallins are divided into alpha, beta, and gamma families. Alpha crystallins are composed of two gene products: alpha-A and alpha-B, for acidic and basic, respectively. Alpha crystallins can be induced by heat shock and are members of the small heat shock protein (HSP20) family. They act as molecular chaperones although they do not renature proteins and release them in the fashion of a true chaperone; instead they hold them in large soluble aggregates. These heterogeneous aggregates consist of 30-40 subunits; the alpha-A and alpha-B subunits have a 3:1 ratio, respectively. Two additional functions of alpha crystallins are an autokinase activity and participation in the intracellular architecture. The encoded protein has been identified as a moonlighting protein based on its ability to perform mechanistically distinct functions. Alpha-A and alpha-B gene products are differentially expressed; alpha-A is preferentially restricted to the lens and alpha-B is expressed widely in many tissues and organs. Elevated expression of alpha-B crystallin occurs in many neurological diseases; a missense mutation cosegregated in a family with a desmin-related myopathy. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2019]
Muuta tietoa krystalliineista:
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3554465/
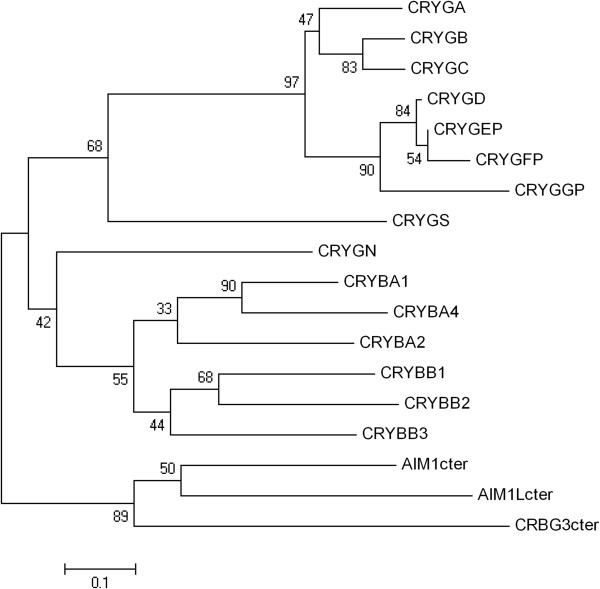
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic tree of the humanβγ-crystallin gene superfamily. Sequences were extracted from the UCSC web browser. Translated ORFs were aligned and neighbor-joining trees were constructed as in Figure 2. AIM1, AIML, and CRYBG3 contain internal repeats corresponding to three β-crystallin-like genes in addition to regions not related to crystallin genes. For simplicity, the third, most highly conserved crystallin repeat from each gene was used for this alignment (designated AIM1cter, etc.).
CRYB genes
This multigene family has ancient origins in vertebrates, and indeed the six human genes have clear orthologs in fish [28]. β-crystallins are subdivided into acidic (A) and basic (B) subunits, encoded in CRYBA(12,4) and CRYBB(123) genes. Unlike the α-crystallins, four of the β-crystallin genes, arranged as two pairs, are close together on Chr 22 (Table 1, Figure 4).
Table 1.
Human lens crystallin genes
Crystallin genes Chr α-crystallins
CRYAA/αA
21q22.3
CRYAB/αB
11q23.1
β-crystallins
CRYBA1/βA1, βA3
17q11.2
CRYBA2/βA2
2q35
CRYBA4/βA4
22q12.1
CRYBB1/βB1
22q12.1
CRYBB2/βB2
22q11.3
CRYBB2 P1
22q11.3
CRYBB3/βB3
22q11.23
γ-crystallins
CRYGA/γA
2q34
CRYGB/γB
2q34
CRYGC/γC
2q33.3
CRYGD/γD
2q33.3
CRYGEP/γE
2q33.3
CRYGFP/γF
2q34
CRYGS/γS
3q27.3
CRYGN/γN
7q36.1
CRYGGP
2p16.3
‘Enyzme-crystallin’
BHMT/ψ 5q14.1 Gene/protein names and chromosome locations are shown. Genes/proteins in bold type are expressed at relatively high levels similar to orthologs in other mammals. Those in normal type seem to have reduced or no expression in human lens. Some are designated pseudogenes. The proposed crystallin designation for betaine-homocysteine methyltransferase (BHMT), ψ, does not imply pseudogene status.
Inga kommentarer:
Skicka en kommentar