http://www.fineli.fi/food.php?foodid=322&lang=fi
Kukkakaalissa on hieman myös proteiinia, muta sen määrä on niin pieni, että vaikka se sisältää puriinia, se ei enää mainita kiellettynä kihtipotilaan dieetissä: Kts. http://www.terveyskirjasto.fi/terveyskirjasto/tk.koti?p_artikkeli=dlk00032
Näiden taulukoitujen ravinteiden lisäksi on kukkakaalissa Brassica oleracea myös jollain tavalla hyödyllisiä muitakin molekyylejä kuten glukosinolaatteja ja karotinoideja.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucosinolate
- Artikkeli kaalien glukosinolaateista:
Phytochemistry. 2012 Jan;73(1):74-83. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2011.09.010. Epub 2011 Oct 24. Establishing the occurrence of major and minor glucosinolates in Brassicaceae by LC-ESI-hybrid linear ion-trap and Fourier-transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry.
Tiivistelmä, Abstract
- GLUKOSINOLAATIT (GLS) ovat rikkipitoisten kasvien sekundaarisia metabolisia tuotteita ja niitä on kaalikasveissa koko joukko erilaisia. Brassica suvussa on iso fytokemikaalien perhe eri runsausastein.
- Määritettiin parsakaalista ja kukkakaalista sekä eräästä salaattilajista näitä fytokemikaaleja.
- Brassicaceae- laajeilla havaittiin kahdeksan vähäisen määrän glukosinolaatia: 1- metyylipropyyli GLS, 2-metyylipropyyli-GLS, 2-metyylibutyyli-GLS, 3-metyylibutyyli-GLS, n-pentyyli-GLS, 3-metyylipropyyli-GLS, 4-metyylipentyyli-GLS ja n-hexyyli-GLS. Nämä glukosinolaatit kuuluvat perheeseen, jossa on tyydytetty alifaattinen sivuketju kokoa C(4), C(5) ja C(6). Sivuketjut muodostuvat oletettavasti aminohappo esimuodoista leusiinista, homoleusiinista ja dihomoleusiinista ketjun pidentymillä
- Näitä esiintyi sekä kukkakaalissa, parsakaalissa että mainitussa slaattityypissä.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
- GLUKOSINOLAATIN RAKENNE:(Wikipediasta oleva kuva)

- GLUKOSINOLAATTIEN tarkoitus kasveissa lienee olla niiden suojamolekyyli.Asiaa voi jopa hyödyntää kuten linkki osoittaa: http://www.mtt.fi/met/pdf/met10a.pdf
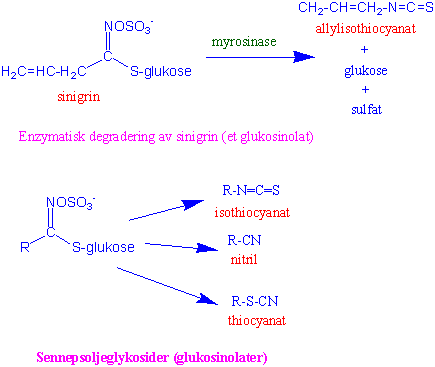
- GLUKOSINOLAATTI on toiselta nimeltään sinappiöljyglykosidi. Kaava glukosinolaatin hajoamisesta entsymaattisesti.http://www.mn.uio.no/ibv/tjenester/kunnskap/plantefys/leksikon/g/glukosinolat.html
Inga kommentarer:
Skicka en kommentar